Whenever you manage users who require access to multiple types of data in order to do their job or purchase a product, you need a strong set of standards to help you implement access controls and protect your information systems from cybersecurity threats. This is commonly known as Identity and Access Management (IAM). Not only does IAM grant secure access to what you and your applications do, it also grants access to the many service-to-service calls that occur behind the scenes. An example of IAM in action is Amazon Web Service (AWS) IAM service handling more than 400 million API calls per second worldwide. Nonetheless, even if your organization only handles a single call per second, or minute, or even hour, IAM has never been more important than present day.
So, what is IAM?
Identity Access Management (IAM) is a growing field focused on ensuring that data shared across your organization is accessible to the right people, and remains inaccessible to those who should not have access to it. Gartner1 sums it up by saying that a good IAM program “enables the right individuals to access the right resources at the right times for the right reasons.” IAM enables you to:
- Manage IAM users and their access: You can create users in your identity management system, assign users individual security credentials (such as access keys, passwords, multi-factor authentication devices), or request temporary security credentials to provide users access to services and resources. You can specify permissions to control which operations a user can perform.
- Manage access for federated users: You can request security credentials with configurable expirations for users who you manage in your corporate directory, allowing you to provide your employees and applications secure access to resources without creating a user account for them. You specify the permissions for these security credentials to control which operations a user can perform.
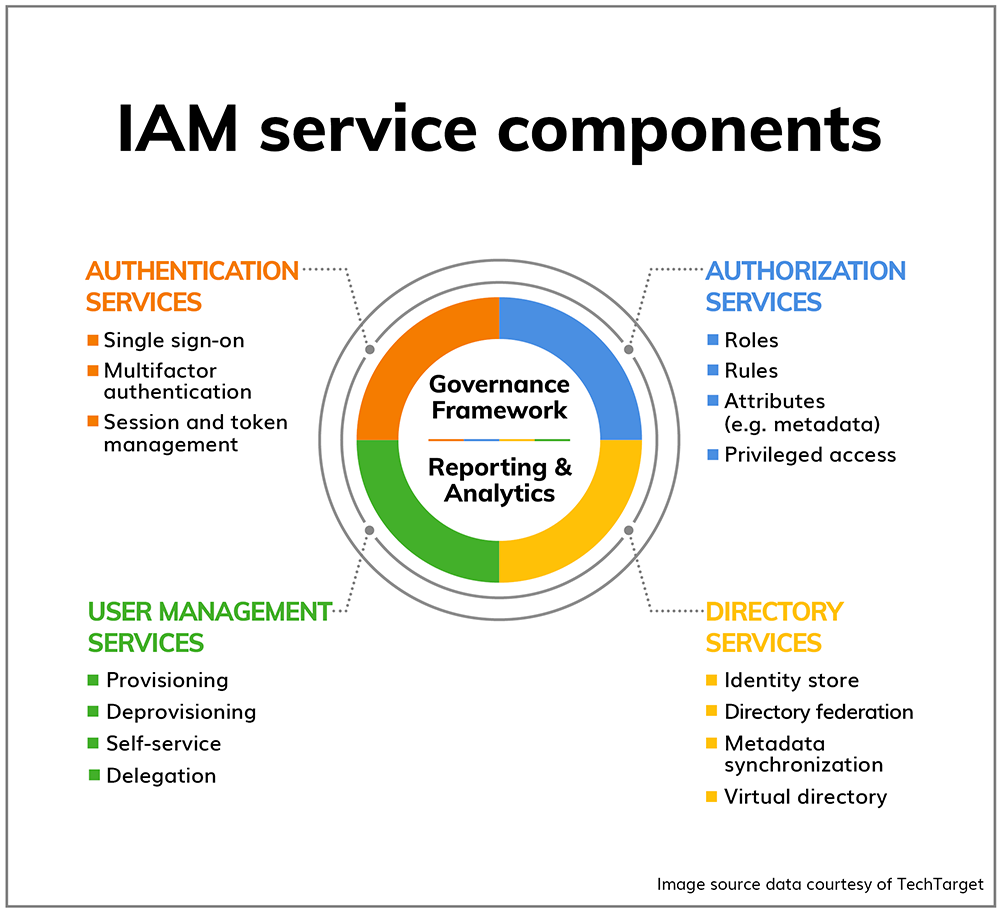
Most IAM solutions centralize the key pillars shown in the image below:
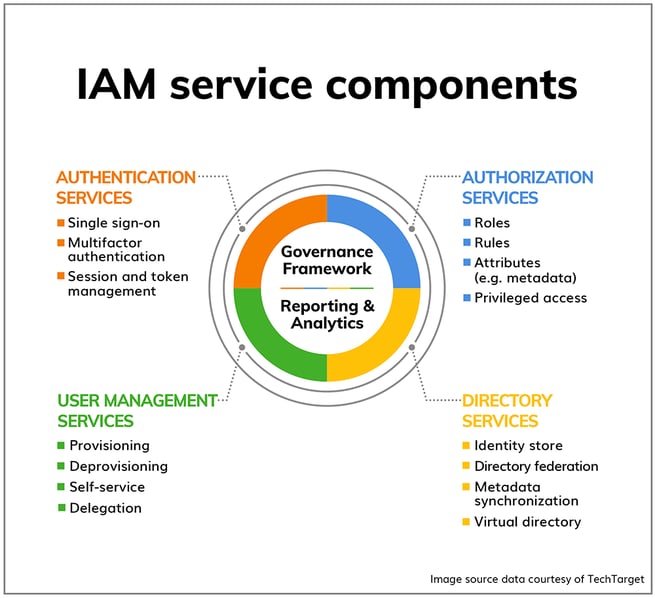 Image source2 |
- Identity - a factor that can be used to recognize a person or a device in the enterprise
- Authentication - the procedure of uniquely distinguishing a person or a device
- Authorization - the process of giving someone permission to do or to have something
- Directory - where the user is stored and can we connect to other stores-federation
When considering user profiles in Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions, there are several ways of defining the user, risk, and resource requirements, I like to narrow it down to two key types.
- Role-Based Access Control vs Attribute-Based Access Control
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), an access control method that provides access rights depending on the user’s role in the organization, is the most common type of access control and the simplest to deploy.
Attributes Based Access Control (ABAC) grants access rights to the user by using a combination of attributes together. ABAC is the most flexible, but also the most complex. ABAC enables refined access control that allows for more input variables into an access control decision and requires input from various business units in your organization to successfully implement. An example of ABAC would be allowing only users who are “type=employees” in “department=HR” access to the HR/Payroll system and only during business hours within the same time zone as the company.
2. Cloud Identity and Access ManagementCloud computing is a rapidly growing architecture that challenges enterprise administrators with varying workloads, data lakes3, and user requirements that can create vulnerabilities to various kinds of network attacks and privacy issues. With its cost-effectiveness and flexibility, cloud networks in the public sphere can create more challenges; whereas the public cloud provider creates a “walled garden” for their infrastructure and the enterprise administrator provides the security to the data property within. In this, it is necessary to have Identity and Access Management.
Cloud IAM tools allow administrators to authorize who can access specific resources at specific times via a specific way by giving the enterprise administrator full control and visibility to manage their cloud resources. In some cases, Cloud IAM can provide control for software as a service (SaaS) based applications for even more granular control. With any Cloud IAM tool, you will want it to provide a unified view into security policy across your entire organization and have built-in auditing that can ease compliance processes.
Most-impactful benefits of using IAM system for the enterprise:- Single access to all enterprise resources (SSO)
- Enhanced centralized privilege management: The right person in the right area.
- Enhanced centralized security
- A single data source for HR (Human Resources)
- Centralizing auditing and logging
- Easy to manage privileges for enterprise employees
- Easy to integrate with other enterprise software and mobile applications
- Avoid accounts overlapping for enterprise systems
- Audit, track, monitor, and report users activities
- Better compliance
For a more specialized approach, users can take advantage of third-party products, which provide IAM for cloud-based applications. Some enterprises have built their own IAM by taking advantage of various open source technologies, though this approach can be more complex. And even with targeted solutions, there is still the challenge with identifying every aspect within your organization which needs access control while also maintaining compliance and interoperability with legacy systems.
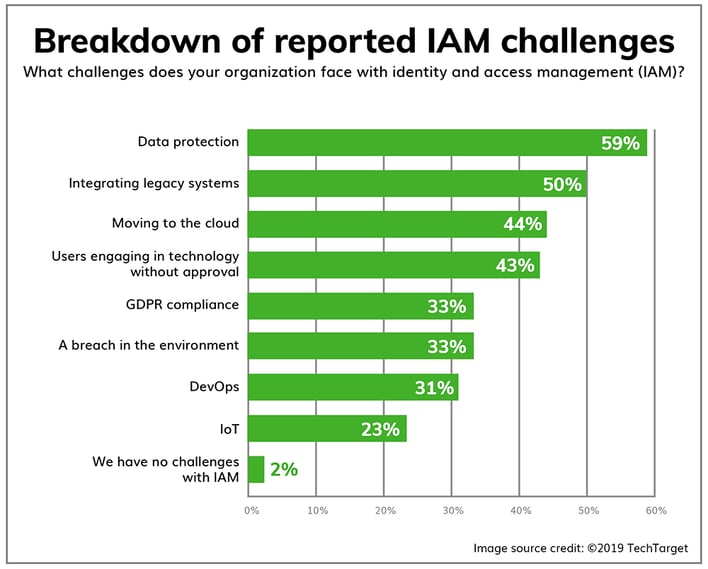 Image source2 |
This is why IAM, like any form of security, is a journey and is constantly evolving. As stewards of this task within the organization we must continuously be ever vigilant and evolving as all aspects evolve with time.
Enterprises around the world must ensure employees, customers, and business partners all have proper access to information and technology resources in a secure, fast and efficient manner. By implementing Identity Access Management tools and following related best practices, a company can gain a competitive edge by enabling better collaboration, enhanced productivity, increased efficiency, and reduced operating costs.
Read Part 1 of this series: Preparation and strategy for cloud security
Read Part 3 of this series: Threat detection and initial response in the cloud.
1Gartner Information Technology Glossary, Gartner, Inc., 2022 https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/identity-and-access-management-iam
2Gittlen, S, Rosencrance, L, What is identity and access management? Guide to IAM, TechTarget, 2019 https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/identity-access-management-IAM-system
3What is a data lake?, Amazon Web Services, Inc., 2022 https://aws.amazon.com/big-data/datalakes-and-analytics/what-is-a-data-lake/